|
(Clicking
on the thumbnail images below will launch a new window and a larger
version of the thumbnail.)
|
| Last updated: |
| Oct 27, 2005. |
Rattus norvegicus
Order: Rodentia
Family: Muridae
1) General Zoological Data
The common laboratory rat (or brown, Norway rat) originated perhaps in China and is now widely disseminated throughout the world. There are at least 56 nominated, different species of Rattus (Nowak, 1999), the Norway rat having presumably derived from Rattus rattus. So stated Kohn & Barthold (1984) in a comprehensive chapter on all aspects of rat biology. Nowak (1999) suggested that the Norway rat did not reach Europe until 1553, and the Americas until 1750. With its arrival, local populations of rats have become reduced in number or have become extinct.
 |
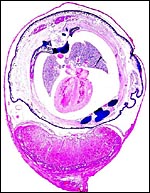
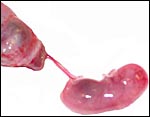
Pregnant laboratory rat. |
Laboratory rats have bicornuate uteri and weigh between 200 and 400 g. There are numerous different "strains" with slightly different gestational features. A commonly used animal is the Wistar rat; it is white in color. Another important strain is the Sprague Dawley rat, but many more well-known strains are also employed for research purposes. Estrus lasts 20 hours, and the gestation lasts 21-26 days (generally 22 days). The litter size varies from 2 to 22 but is usually around 10. Neonates weigh between 5 and 7 g, are blind until their lids open at 15 days, and they are weaned at 22 days. Sexual maturity is attained in 2-3 months. The 20-day pregnant female shown here weighed 340 g, and the average near-term pup was 6.3 g. It had 9 fetuses, evenly spaced in the bicornuate uterus. Another specimen studied was late on day 14 (to 15) and had 13 fetuses. Numerous details on breeding, artificial insemination, cycles, etc. are supplied by Kohn & Barthold (1984).
3) Implantation
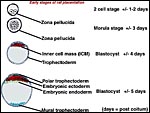
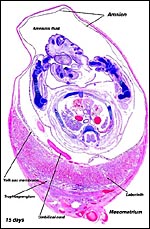
The first major description of rat (and mouse) placentation is that by Duval (1891) which is followed by numerous additional studies, including the employment of histochemistry, fine structural analysis and studies of the placental/uterine vasculature. The initial implantation is antimesometrial and early development is quite similar to that of the mouse, as has been mentioned by several authors. For that reason, some of the diagrams used in the mouse chapter are employed here as well. Moreover, some details of placental development detailed there are not repeated in this chapter.
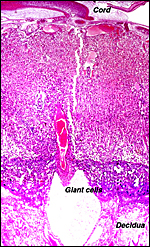
The fertilized ova arrive in the uterus as blastocysts about 3-(4) days after mating and implant in regularly spaced intervals, helped presumably by uterine contractions, on day 5. Initially, the blastocyst is surrounded by a single layer of trophoblast but on day 8 a preplacental cone (the "Träger") of trophoblastic proliferation develops opposite the implantation site whence the placental disk forms. At its periphery, giant trophoblast cells become apparent that mingle with the decidua and have phagocytic activity. As in the mouse, an "ectoplacental" cone develops in an endometrial space and a peripheral trophoblastic giant cell zone develops. This is followed by the ingrowth of allantoic vessels and cells that ultimately form the placental labyrinth of the disk. The giant cell zone is subtly admixed with decidual cells and becomes displaced by the mesometrially developing labyrinth; it breaks up on day 17.
Enders & Schlafke (1967) have studied in great detail the initial implantation and the decidual reaction. Because the endometrial reaction is mimicked in studies employing inert objects rather than blastocysts (Blandau, 1949), and for reasons of edema in the decidua, Enders & Schlafke speak of endometrial "clasping" of the blastocyst and liken it to the irritation by an inert object.
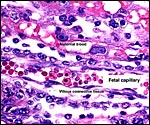
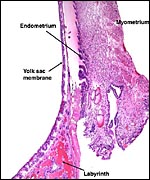
Rats have an inverted yolk sac placenta with a disk that is labyrinthine and has a hemotrichorial fine-structure. The placenta is discoid and ends up at the mesometrial uterine side. As mentioned earlier, many aspects of rat placental development are very similar to those described for the mouse. They have been described in great detail by deRijk et al. (2002), a publication that provides ready access to most important features. That detailed description elaborates on every day of development and it includes color photomicrographs. The mechanism of protein transport to the fetus ("embryotrophic nutrition") was studied by Beck et al. (1967) and many other investigators as well. Beck et al. showed by injecting horseradish peroxidase into maternal vessels that proteins reach the fetus via the visceral layers of the inverted yolk sac membranes following digestion in the lysosomes. The labyrinthine trophoblast did not transport these substances.
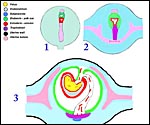
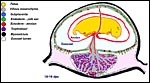
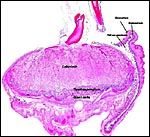
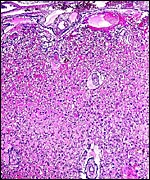
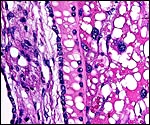
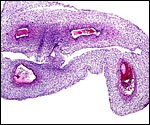
The different layers of placental development are shown in the next few photographs. They show the three principal regions of the placental disk: From the fetal surface the chorioallantoic connective tissue extends into the labyrinth which is the major portion of the disk. This is followed by the less differentiated trophoblast of the trophospongium and, at the base, the giant cell layer that interdigitates with the decidua is apparent. The cells of the trophospongium are relatively uniform and vacuolated, presumably precursor cells of a more differentiated trophoblast. Detailed histochemical and fine-structural studies are found by Schiebler & Knoop (1959). Of special interest is their study of Reichert's membrane and the "membrane" developing at the base of the disk, a fibrous-appearing irregular structure that develops during gestation.
Fine structural details have been delineated by numerous investigators (Schiebler & Knoop, 1959; Jollie & Benscome, 1965; Enders & Schlafke, 1967; Franke, 1969; Martinek, 1970; Lee & Dempsey, 1979). A very detailed account of the sequence of rat placental development is found by Wooding & Flint (1994). In their description there is a special consideration of the function and denomination (Layers I-III) of the three layers of trophoblast, their development and their possible interference with fetal blood flow.
More recently, attention has been paid to the genetic regulatory mechanisms of trophoblast development. A huge literature is thus developing that can, in part, be accessed at the internet through Medline ("PubMed"). For instance, Ma et al. (2001) showed that "nodal" is expressed in the (mouse) placenta, especially in spongiotrophoblast. When null mutants are used, there is a significant disruption of embryonic and placental developments with expansion of the polyploid giant cell layer. Ohgane et al. (2002) investigated the differential methylation patterns of developing trophoblast by using rat cell lines that differentiate into giant cells. They identified cells that lost their methylation patterns during differentiation. Zybina & Zybina (2000) and Zybina et al. (2000) showed endoreduplication up to octoploid levels in the giant cells and correlated this with their phagocytic activity during the process of decidual and vascular invasion. Dupressoir et al. (2005) provided evidence for the concept that two retrovirus envelope protein genes, different from those in primate placentation, led to the production to the trophoblastic giant cells.
Parast et al. (2001) showed in primary trophoblast and rat choriocarcinoma cell lines that the initially unicellular trophoblast was mobile but when it underwent polyploidization, marked cytoskeletal changes occurred concurrent with cellular immobility. The enormous number of these modern studies cannot be dealt with here and must be studied in the original contributions. The limited life span of rat trophoblastic giant cells (decrease after day 17 and disappearance at term) was attributed to programmed cell death (apoptosis) in the study of Dorgan & Schultz (1971).
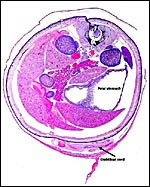
6) Umbilical cord
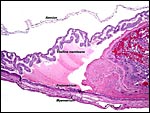
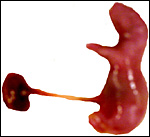
The length of the umbilical cord was measured throughout gestation by Fujinaga et al. (1990). It had a linear growth from 0.5 cm at 13 days to 3 cm at day 20. They suggested that, because of this linear growth, the common stretch hypothesis of cord growth was invalid. Other findings, especially from other mammals, however, argue against this interpretation. The umbilical cords of my fetuses measured between 1.5 and 2.3 cm in length, had no spirals and were extremely delicate. The surface of the umbilical cord is a single layer of amnionic epithelium. There are two portions of cord, each having two vessels. The cord length that has been just referred to is that of the chorioallantoic portion. The more delicate vitelline cord stretches over the membranous dome to the yolk sac. Its course can be seen in the diagram and pictures shown below.
Interestingly, there was a reduction of the length of umbilical cords when rats were made diabetic during gestation (Padmanabhan & Shafiullah, 2001).
The complex blood flow through the rodent placenta was beautifully diagrammed by Mossman (1987) and is shown in a subsequent diagram. The microcirculation of the rat placenta has been detailed in a study of preparing casts and scanning electronmicroscopy by Lee & Dempsey (1976). The rat uterus is supplied by an arcade of arteries that originate both from the uterine distal pole and the cervical region. This arrangement has allowed Wigglesworth (1964) to experiment with the aim at understanding fetal growth restriction. When one end of the arcade only was ligated, the embryos near the ligation site were severely growth-restricted and then became gradually more normal in size the closer they were situated towards the unligated artery.
 |
Central maternal artery as it enters through the giant cell layer and enters the labyrinth. |
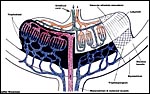 |
Maternal and fetal vascular blood flows of the rodent placenta (modified from Mossman). |
Amniogenesis is by "cavitation" and there is an initially bilaminar yolk sac. It gets to be stretched enormously half-way through gestation and, at the dome of the organ, it becomes exceedingly thin. There is only a vestigial allantoic sac. The endometrial epithelium undergoes degeneration over most of the implantation site.
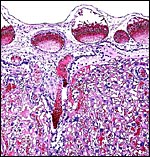
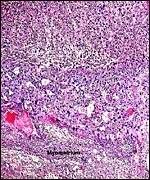
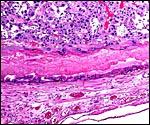
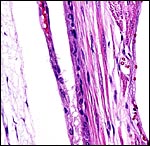
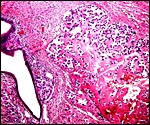
As in primates and many other rodents, trophoblast infiltration of the decidua and uterine arteries occurs in the rat. The evolution of the intra-arterial trophoblast proliferation was studied in several contributions by Legrand (e.g., 1974) who described it as deriving from primitive trophoblast on day 10-11. More recently, Caluwaerts et al. (2005) described the trophoblastic infiltration as occurring all the way up into the vessels of the mesometrial triangle; they also studied the modulation of these maternal blood vessels, and the associated maternal lymphocyte infiltration. The latter contributions are available in abstract form only at this time and will be of future interest when published in full. The vascular infiltration of vessels was described to commence after day 15 and there ensued a significant alteration of the muscular wall, with stimulation of the endothelium. The extensive trophoblast invasion of the maternal blood vessels was not present in the two uteri that I have been able to study and I wonder whether this may be strain-dependent. While there was infiltration of the maternal arteries at the point of decidual implantation, it did not pursue to deeper levels of the arterial lumens. Instead, the arteries were modified by the infiltration of large cells with conspicuous eosinophilic granules as shown below. These did not have the appearance of trophoblast; the vascular endothelium was intact - although hypertrophied - and was not altered by trophoblastic infiltration. The appearance of these granulated cells was more like that of the "granulated metrial cells" discussed in some detail by de Rijk et al. (2002).
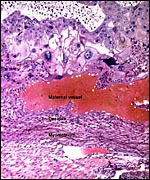 |
Invasion of maternal blood vessel by trophoblast at 15 days. |
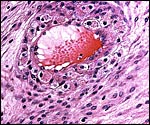 |
Maternal arteriole with modification of its muscular wall by infiltrating granulocytic cells. |
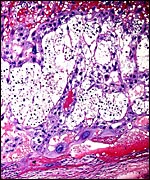
There is extensive decidualization around the time of implantation, commencing around blood vessels and reaching its height at 5 days. This aspect has been studied by many investigators in detail and was admirably summarized by Enders & Schlafke (1967). This publication includes a discussion of the development of pseudodecidua upon mechanical stimulation. De Rijk et al. (2002) described two distinct types of decidual cells whose prevalence varies with advancing gestation. The "decidualized" stromal cells contain abundant glycogen. The fact that a pseudodecidua is readily induced in the rat by hormonal and mechanical stimuli has been well known for many years and was then studied electronmicroscopically in some detail by Jollie & Benscome (1965). These authors also reviewed the older description of decidualization in rat pregnancy. Cellular enlargement and development of binucleation were prominent findings. Lipids and glycogen become prominent components as the stromal cells assume an epithelioid appearance. Martinek (1970) observed that the basal "fibrinoid" that is found beneath the implanted disk is never a complete barrier between trophoblastic base and decidua. The observation that rats have a decidua was a focal point for Thomas Huxley in his debate with Richard Owen when the former advocated the use of placentation for phylogenetic considerations. This has been beautifully recounted in a recent contribution by Pijnenborg & Vercruysse (2004). Their brief discussion of this is well worth reading, if only for historical reasons.
The observation that rats have a decidua was a focal point for Thomas Huxley in his debate with Richard Owen when the former advocated the use of placentation for phylogenetic considerations. This has been beautifully recounted in a recent contribution by Pijnenborg & Vercruysse (2004). Their brief discussion of this is well worth reading, if only for historical reasons.
11)
Various features
There is no true subplacenta in this myomorph rodent as is seen in the
caviomorph rodents.
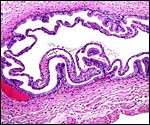
In the absence of mating, fully-functional corpora lutea are not produced in this spontaneous, polyestrous ovulator. When pregnancy ensues, however, the corpus luteum is activated and it is then being maintained by as yet incompletely understood endocrine mechanisms. Estradiol, rather than LH is necessary for its function as well as prolactin. For the corpus luteum to be sustained and thus to produce the needed progesterone for the maintenance of gestation, the decidua and trophoblast produce prolactin-like hormones. The placenta does not produce progesterone but may elaborate some androgens. Luteolysis is accomplished by prostaglandins (Juengel et al., 1999). Numerous other studies of endocrine parameters are summarized in chapters of the "Encyclopedia of Reproduction" by Knobil & Neill (1999).
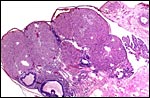 |
Ovary with several corpora lutea and a few Graafian follicles. Fallopian tube at right. |
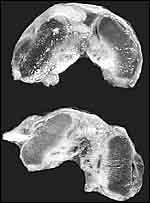
The laboratory rat has 42 chromosomes. There is now an extensive literature on this species' chromosomes; much of the older literature was listed in Hsu & Benirschke (1967). The standardization of the rat chromosome nomenclature was achieved in 1973 (Committee, 1973). Robertsonian fusion has been described by Bretfeld (1968). Other polymorphisms have been described, as were the numerical chromosomal errors that occur in various tumors.
In addition to the laboratory rat, Rattus rattus, the black rat, has evolved many different karyotypes during their distribution over Oceania, mostly by Robertsonian fusion of chromosomes. Chromosome painting of the black rat (2n=38) was undertaken by Cavagna et al. (2002) and compared with mouse and Norway rat. Details and references may there be found. Although many rodents were used for attempts at hybridization with the Norway rat, most have been unsuccessful (Gray, 1972).
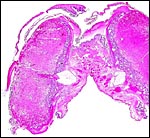
A very large number of rat diseases are known, in addition to a variety of genetic syndromes. For instance, the equivalent of the heritable human testicular feminization syndrome (androgen insensitivity - X-linked trait) exists in rats and in a few other species. Females have testes but lack uteri (Bullock, 1979). Another remarkable "animal model" is the Brattleboro rat with diabetes insipidus (Sokol & Valtin, 1982). Likewise, diabetes mellitus has been studied extensively in an inbred strain of rats (Shafrir & Renold, 1988). When rats were treated with streptozotocin in early gestation, fetuses were growth-restricted unless the dam was treated with insulin; minor developmental defects developed in the fetuses. In addition, the giant cell layer proliferated enormously and numerous glycogen-laden cells were found in the decidua and other regions of the placenta (Padmanabhan & Shafiullah, 2001). Exposure to cigarette smoke during gestation was found to have a significant effect on the size of labyrinthine giant cells in the placenta, as well as measurable changes in fetal organ development (Czekaj et al., 2002). Spontaneously hypertensive rats (during pregnancy) have been developed (see section on physiology). Syncytin-A and –B, fusogenic placenta-specific murine envelope genes, were detected by Dupressoir et al. (2005).
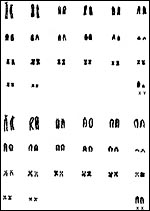 |
Karyotype of laboratory rats, Rattus norvegicus. |
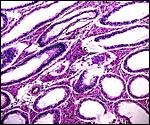 |
Testis of adult rat with "testicular feminization". I.C. = interstitial cells. |
Caluwaerts (2005) addressed the modulation of decidual lymphocytes during trophoblast infiltration. Brambell (1954) and Bainter (1986) have shown immune globulin protein transport across the vitelline membranes.
15)
Pathological features
Aside from its own infectious diseases, the Norway rat has been instrumental
in the dissemination of numerous human infectious diseases. Among the
best-known is the bubonic plague; others are listed by Nowak (1999) and
by numerous other authors.
An "intersexual" rat with ovary, ovotestis, left uterus and
male external genitalia was described by Burrill et al. (1941). When rat
fetuses die prior to delivery, they may be resorbed, and a space is found
at the site of former implantation with a "scar" that is usually
pigmented. Conaway (1955) studied these pigmented (hemosiderin) scars
and found them to persist for a year. Placental tissue was not found.
He found spontaneously-developing scars, and he also caused the scar development
by colchicines injection into fetal cavities that resulted from fetal
demise. Remarkably, term fetal development has occurred in an extrauterine
implantation (Gosden & Russell, 1981). The fetus was dead but normally
developed (4.83 g) and the placenta weighed 2.5 g. It had implanted on
the omentum, and the uterus was not impaired. Thus, this must have been
a primary extrauterine gestation that had formed in the absence of decidua,
similar to what has been observed in human gestations. Others have shown
that extrauterine development is possible, as referenced by Enders & Schlafke (1967). A completely fused placenta with two female fetuses was
described by Arora (1977). The labyrinths were separated by a septum of
giant cells; their zygosity remained unknown.
16)
Physiologic data
Disappointed by the absence of detailed information, deRijk et al. (2002)
have described in precise details the hematologic findings, clotting features
and other aspects of rat placentation as well as the general physiologic
changes occurring during pregnancy. Another large review of many physiologic
features is by Kohn & Barthold (1984). Wang et al. (2002) deduced
from their study of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor (PPAR)
and the 9-cis retinoic acid receptor (RXR) isoforms in the labyrinth their
contribution to the transfer of the regulation of fatty acid metabolism
and transport.
A model of spontaneous hypertension in pregnancy was studied in a special
strain of rats by Sharkey et al. (2001). This assumes importance because
of the prevalence for this common human gestational complication. Although
no structural changes were observed as a result of the hypertension in
fetal organs or placenta, several physiological changes occurred that
simulated human pre-eclampsia. L-arginine administration to the drinking
water prevented hypertension, especially in the third trimester. Wlodek
et al. (2001) further studied this model by embryo transfers and found
fetal growth restriction and deficiency of amnionic fluid. They were thus
able to attribute this to fetal, rather than maternal influences.
The receptor for pituitary adenyl cyclase polypeptide (PACAP) was expressed
initially in the decidua and later in chorionic blood vessels and also
in villous stromal cells, suggesting that it has an important regulatory
function (Koh et al., 2003).
Senut et al. (1998) injected genetically altered rat and human cells into
the placental disks of pregnant rats to study possible gene transfer.
Many abortions occurred when injections were done before day 16, but at
later gestation, the embryos and placental grafts survived. They showed
that hGH-secreting cells delivered their product into the fetal circulation.
17)
Other resources
Numerous cell lines of various tumors and modified cell types are available
for different rat strains. Some, for instance, are available by logging
on to "RIKEN" and searching their cell/animal catalogue.
Acknowledgement
I am most appreciative to Dr. Michael Oldstone of Scripps Institution
for Research in La Jolla and to Drs. A. & N. Varki.
References
Arora, K.L.: A case of placental fusion in a Sprague Dawley rat. Lab.
Anim. Sci. 27:377-379, 1977.
Bainter, K.: Intestinal absorption of macromolecules and immune transmission from mother to young. CRC Press, 1986.
Beck, F., Lloyd, J.B. and Griffiths, A.: A histochemical and biochemical study of some aspects of placental function in the rat using maternal injection of horseradish peroxidase. J. Anat. 101:461-478, 1967.
Blandau, R.J.: Embryo-endometrial interrelationship in the rat and guinea pig. Anat. Rec. 104:331-359, 1949).
Brambell, F.W.R.: Transport of proteins across foetal membranes. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 19:71-81, 1954.
Bretfeld, G.: Heterozygote Zentrenfusion bei einer weissen Laborratte. Experientia 24:724, 1968.
Bullock, L.P.: Testicular feminization (androgen insensitivity). Chapter 78, pp. 190-191, in, Andrews, E.J., Ward, B.C. and Altman, N.H.: Spontaneous Animal Models of Human Disease. Vol. 1. Academic Press, NY, 1979.
Burrill,
M.W., Greene, R.R. and Ivy, A.C.: A case of spontaneous intersexuality
in the rat. Anat. Rec. 81:99-117, 1941.
Caluwaerts, S., Vercruysse, L., Luyten, C. and Pijnenborg, R.: Endovascular trophoblast invasion and associated structural changes in uterine spiral arteries of the pregnant rat. Placenta 26:574-584, 2005.
Cavagna, P., Stone, G. and Stanyon, R.: Black rat (Rattus rattus) genomic variability characterized by chromosome painting. Mammal. Genome 13:157-163, 2002.
Committee: Standard karyotype of the Norway rat, Rattus norvegicus. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 12:199, 1973.
Conaway, C.H.: Embryo resorption and placental scar formation in the rat. J. Mammal. 36:516-532, 1955.
Czekaj, P., Palasz, A., Lebda-Wyborny, T., Nowaczyk-Dura, G., Karczewska, W., Florek, E. and Kaminski, M.: Morphological changes in lungs, placentae, liver and kidneys of pregnant rats exposed to cigarette smoke. Int. Arch. Occup. Environm. Health. 75 (Suppl. 1):27-35, 2002.
deRijk, E.P.C.T., van Esch, E. and Flik, G.: Pregnancy dating in the rat: placental morphology and maternal blood parameters. Toxicologic Pathol. 30:271-282, 2002.
Dorgan,
W.J. and Schultz, R.L.: An in vitro study of programmed death in rat placental
giant cells. J. Exp. Zool. 178:497-512, 1971.
Dupressoir, A., Marceau, G., Vernochet, C., Bénit, Kanellopoulos, C., Sapin, V. and Heidmann, T.: Syncytin-A and syncytin-B, two fusogenic placenta-specific murine envelope genes of retroviral origin conserved in Muridae. Proceed. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 102:725-730, 2005.
Duval, M.: Le placenta des rongeurs. Le placenta de la souris et du rat. J. Anat. et Physiol. 27:24-73, 1891.
Enders, A.C. and Schlafke, S.: A morphological analysis of the early implantation stages in the rat. Amer. J. Anat. 120:185-226, 1967.
Franke, H.: Feinstruktur der Plazenta. Elektronoptische Untersuchungen über die reifende und reife Plazenta der Ratte. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1969.
Fujinaga, M., Chinn, A. and Shephard, T.H.: Umbilical cord growth in human and rat fetuses: evidence against the "stretch hypothesis". Teratology 41:333-339, 1990.
Gosden, R.G. and Russell, J.A.: Spontaneous abdominal implantation in the rat with development to full term. Lab. Animals 15:379-380, 1981.
Gray, A.P.: Mammalian Hybrids. A Check-list with Bibliography. 2nd edition. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux Farnham Royal, Slough, England, 1972.
Hsu, T.C. and Benirschke, K.: An Atlas of Mammalian Chromosomes. Springer-Verlag, New York. Vol. 1, Folio 18, 1967.
Jollie, W.P. and Benscome, S.A.: Electron microscopic observations on primary decidua formation in the rat. Amer. J. Anat. 116:217-236, 1965.
Juengel,
J.L., McIntush, E.W. and Niswender, G.D.: Corpus luteum. Pp. 703-717,
in, Knobil, E. and Neill, J.D.: Encyclopedia of Reproduction, Vol. 1,
Academic Press, San Diego, 1998.
Kennedy, L.A. and Persaud, T.V.N.: Pathogenesis of developmental defects induced in the rat by amniotic sac puncture. Acta anat. 97:23-35, 1977.
Knobil, E. and Neill, J.D.: Encyclopedia of Reproduction. Academic Press, San Diego, 1998.
Koh, P.O., Kwak, S.D., Kim, H.J., Roh, G., Kim, J.H., Kang, S.S., Choi, W.S. and Cho, G.J.: Expression patterns of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide and its type I receptor mRNAs in the rat placenta. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 64:27-31, 2003.
Kohn, D.F. and Barthold, S.W.: Biology and diseases of rats. Chapter 4 in, Laboratory Animal Medicine. J.G. Fox, B.J. Cohn and F.M. Loew, eds. Academic Press, San Diego, 1984.
Lee, M.M.L. and Dempsey, E.W.: Microcirculation of the rat placenta. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic observations on fetal blood vessels. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 126:495-505, 1976.
Legrand, C.: Origine et évolution des cellules trophoblastiques intra-artérielles, chez le rat: etude autoradiographique. J. Embryol. Exp. Morph. 31:693-705, 1974.
Ma, G.T., Soloveva, V., Tzeng, S.J., Lowe, L.A., Pfendler, K.C., Iannacone, P.M., Kuehn, M.R. and Linzer, D.I.: Nodal regulates trophoblast differentiation and placental development. Dev. Biol. 236:124-135, 2001.
Martinek, J.J.: Fibrinoid and the fetal-maternal interface of the rat placenta. Anat. Rec. 166:587-604, 1970.
Mossman, H.W.: Vertebrate Fetal Membranes. MacMillan, Houndmills, 1987.
Nowak, R.M.: Walker's Mammals of the World. 6th ed. The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, 1999.
Ohgane, J., Hattori, N., Oda, M., Tanaka, S. and Shiota, K.: Differentiation of trophoblast lineage is associated with DNA methylation and demethylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290:701-706, 2002.
Padmanabhan, R., Al-Zuhair, A.G.H. and Hussein, A.: Histopathological changes of the placenta in diabetes induced by maternal administration of streptozotocin during pregnancy in the rat. Con. Anom. 28:1-15, 1988.
Padmanabhan, R. and Shafiullah, M.: Intrauterine growth retardation in experimental diabetes: possible role of the placenta. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 109:260-271, 2001.
Parast,
M.M., Aeder, S. and Sutherland, A.E.: Trophoblast giant-cell differentiation
involves changes in cytoskeleton and cell motility. Developm. Biol. 230:43-60,
2001.
Pijnenborg, R. and Vercruysse, L.: Classics revisited. Thomas Huxley and the rat placenta in the early debates on evolution. Placenta 25:233-237, 2004.
Pijnenborg, R., Vercruysse, L., Caluwaerts, S., Verbist, L. and van Assche, F.A.: Placental bed arterial changes related to endovascular and interstitial trophoblast invasion in the rat. Placenta 22:A39 (Abstract P123), 2001.
Schiebler, T.H. and Knoop, A.: Histochemische und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an der Rattenplazenta. Z. Zellf. 50:494-552, 1959.
Senut, M.-C., Suhr, S.T. and Gage, F.H.: Gene transfer to the rodent placenta in situ. A new strategy for delivering gene products to the fetus. J. Clin. Invest. 101:1565-1571, 1998.
Shafrir, E. and Renold, A.E.: Frontiers in Diabetes Research. Lessons from Animal Diabetes II. John Libbey, London, 1988.
Sharkey, L.C., McCune, S.A., Yuan, O., Lange, C. and Fray, J.: Spontaneous pregnancy-induced hypertension and intrauterine growth restriction in rats. Amer. J. Hypertens. 14:1058-1066, 2001.
Sokol, H.W. and Valtin, H.: The Brattleboro Rat. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 394, 1982.
Wang, Q., Fujii, H. and Knipp, G.: Expression of PPAR and RXR isoforms in the developing rat and human term placentas. Placenta 23:661-671, 2002.
Wigglesworth, J.S.: Morphological variations in the insufficient placenta. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Br. Commonw. 71:871-884, 1964.
Wlodek, M.E., Koutsis, K., Westcott, K.T., Ho, P.W., Di Nicolantoni, R. and Moseley, J.M.: The spontaneously hypertensive rat fetus, not the mother, is responsible for the reduced amniotic fluid PTHrP concentrations and growth restriction. Placenta 22:646-651, 2001.
Wooding, F.B.P. and Flint, A.P.F.: Placentation. Chapter 4 (pp.233-460) in, G.E. Lamming, ed. Marshall's Physiology of Reproduction, 4th ed. Vol. 3, Part 1. Chapman & Hall, London, 1994.
Zybina, E.V., Zybina, T.G. and Stein, G.I.: Trophoblast cell invasiveness and capability for the cell and genome reproduction in rat placenta. Early Pregnancy 4:39-57, 2000.
Zybina, T.G. and Zybina, E.V.: Genome multiplication in the tertiary giant trophoblast cells in the course of their endovascular and interstitial invasion into the rat placenta decidua basalis. Early Pregnancy 4:99-109, 2000.